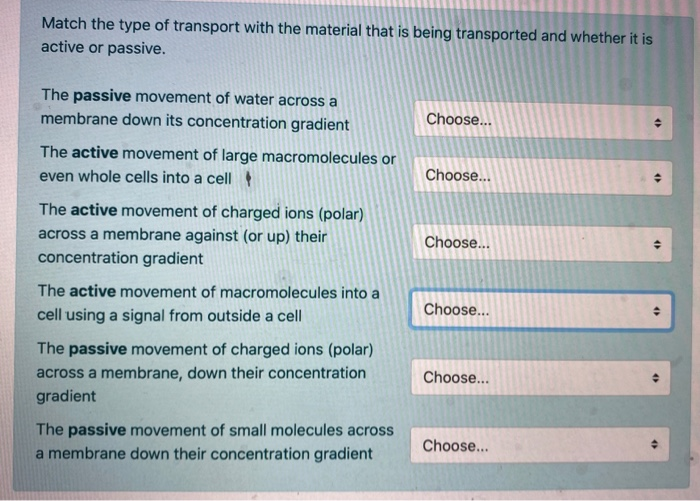
We have discussed simple concentration gradientsdifferential concentrations of a substance across a space or a membranebut in living systems gradients are more complex. You will use each option once Movement of large molecules out of the cell.
Active transport in cell biology refers to the movement of the molecules through the membrane against the concentration gradient which means from an area of lower concentration to an area with higher concentration.

. The most likely mode of transport across the membrane for substance L is active transport. Other mechanisms transport much larger molecules. Engulfing extracellular fluid and numerous dissolved molecules.
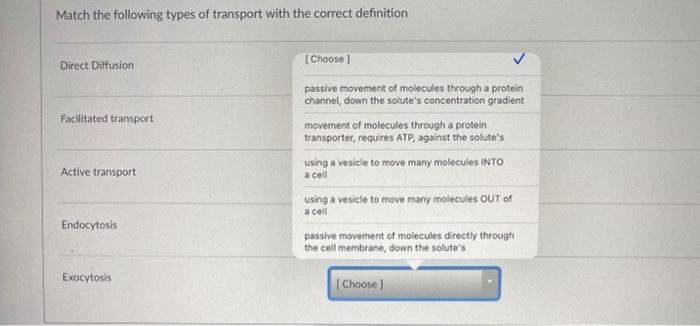
Passive transport is the diffusion of substances across a membrane. Match the modes of transport to the molecules. Thus it requires chemical energy to transport the components from lower to higher concentrated area or body part.
It is the biological process of movement of the molecules against the concentration gradient. Convection is sometimes useful and can be purposefully invoked using a stirbar or a rotating electrode setup but for our purposes it is undesirable and solutions. Convection is the movement of molecules in solution due to random thermal currents.
This is a spontaneous process and cellular energy is not expended. The dashed line is intended to indicate a membrane that is. Polar molecules are soluble in water because the components of the molecule are more strongly attracted to water than to.
The cell membrane controls movement of materials into and out of the cell. Match the items to the correct answers in the key. Movement of particles or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Convection heat transfer occurs partly due to the actual movement of molecules or due to the mass transfer. Look at the diagram of a cross-section of a cell membrane below. The given figure shows transport of two molecules A and B through three different modes of facilitated diffusion.
Active transport Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of. There are three possible ways that molecular transport occurs in an electrolyte solution. Because ions move into and out of cells and because cells contain proteins that do not move.
Select the correct option regarding it. 4 Match the form of bulk transport with the correct description. In contrast potassium and sodium ions move across the nerve membrane against the concentration gradient through transport proteins by active process.
It is the biological process of movements of the biochemical across the cell membranes and tissues. Molecules like glucose move by transport protein by the passive process. Transport of a whole bacteria cell into an animal cell.
The following particles are moving from high concentration to low concentration and are using a carrier protein. The mode of particle transport which needs the input of energy from the cell is called active transport. Tap card to see definition.
Select the correct option regarding it. Heating of milk in a pan. Click again to see term.
Each answer may include more than one item. It is the process in which heat is transferred from one body to another body without involving the. Modes of Transport of different molecules in blood WORKS CITED Polar Molecules Why are Polar Molecules soluble in Water.
Click card to see definition. Molecules will move from where the substance is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated. Migration convection and diffusion.
Active transport moves substances against the concentration gradient from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. Transport of specific large molecules into the cell. Tap again to see term.
This cartoon illustrates passive diffusion.
Solved Match The Type Of Transport With The Material That Is Chegg Com
Solved Match The Following Types Of Transport With The Chegg Com

Solved Match Each Molecule With The Type Of Transport That Chegg Com
0 Comments